Catalytic Converters Replacements
 Canada Custom Mufflers & Brakes offers a wide-range of OBD II compliant universal catalytic converter products which meets stringent EPA and CARB requirements for pollution reduction. Canada Custom Mufflers & Brakes is able to cut and weld on universal Catalytic converter for Cars, Trucks & SUV’s. We carry size from 1.75” to 3.00” to meet your vehicle needs.
Canada Custom Mufflers & Brakes offers a wide-range of OBD II compliant universal catalytic converter products which meets stringent EPA and CARB requirements for pollution reduction. Canada Custom Mufflers & Brakes is able to cut and weld on universal Catalytic converter for Cars, Trucks & SUV’s. We carry size from 1.75” to 3.00” to meet your vehicle needs.
My car did not pass emissions test. Will a new catalytic converter help me?
If the emissions test failure is caused by a bad catalytic converter, then our replacement units will help get the job done. Remember, that when you get a new unit, you need to properly break it in, for it to be effective. We recommend driving for a few hours to heat it up, so that it gives you maximum filtering of your exhaust gases.
Catalytic Converter Symptoms to watch out for:
– Vehicle Losing Power
– Poor Fuel Economy
– Poor Performance
– Rattling Noise From Catalytic Converter Area
– Check Engine Light On
– Failed Emission Test
What is a Catalytic Converter?
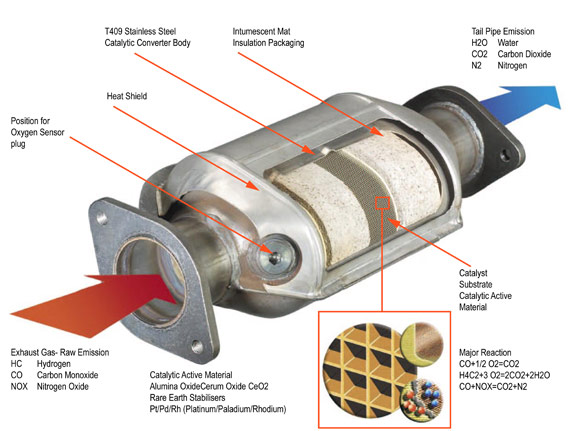
A catalytic converter is a device used to reduce the harmful emissions from an internal combustion engine (used in most modern day automobiles and vehicles). There is not enough oxygen available to oxidize the carbon fuel used in these engines completely into carbon dioxide and water, thus toxic by-products are produced. Catalytic converters are used in exhaust systems to provide a place for the oxidation and reduction of toxic by-products (like nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxides, and hydrocarbons) of fuel into less hazardous substances for the environment such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen gas.
Catalytic converters were first widely introduced in American production cars in 1975 due to EPA regulations on toxic reductions. The United States Clean Air Act required a 75% decrease in emissions in all new model vehicles after 1975. This decrease was to be carried out with the use of catalytic converters. Without catalytic converters vehicles would release hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxide. These gases are the largest source of ground level ozone, which causes smog and is harmful to plant life. Catalytic converters can also be found in generators, buses, trucks, and trains— almost everything with an internal combustion engine will have some sort of catalytic converter attached to its exhaust system.
What is a Catalyst?
It is a thin coating of precious metals (rhodium, platinum and paladium) applied to the surface of the substrate material. Its function is to assist in the chemical reactions that are required to lower the emission levels.
What are Oxidation and Three-Way Converters?
Oxidation converters control two pollutants-carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. These gases come into the converter accompanied by enough oxygen to result in oxidation (burning) by flameless combustion. They pass through the substrate which causes the oxidation process to speed up changing them into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Three-Way converters (also known as Oxidation/Reduction converters) perform the same function as oxidation converters plus they are designed to reduce levels of oxides of nitrogen. Some three-way converters are equipped with an Air Injection Tube. The additional air, which comes from an air pump, assists the chemical reaction in the oxidation catalyst.
Why doesn’t a vehicle pass an Emissions Test?
When a Converter does not function, no exhaust gas conversion takes place. Usually the vehicle will run fine, but it will not pass emission test standards. This may be caused solely by a worn or damaged converter. But, it is difficult to diagnose because it involves other emission system components, as well. The most common cause of this problem is lead contamination within the converter. Use of leaded fuel is usually the source of the contamination.
What makes a Converter become Red Hot?
A Converter will get red hot when raw fuel is introduced directly into it. This is not the problem of the converter itself, but the result of a problem with the fuel system or ignition that allows unburned fuel to pass through the engine to the converter. Possible causes are improper ignition timing, fouled spark plugs, and air pump failure.
What causes a Converter to become clogged?
If a converter is operated too long at a high temperature, its substrate may “melt down” and turn into a solid mass inside the converter. The vehicle may seem sluggish, as if there were a loss of power. Again, an engine and/or fuel system malfunction is allowing a rich fuel mixture to reach the converter. If the problem is not diagnosed and corrected, future converter failures may occur.
Why does the exhaust have a “Rotten Egg” smell?
Many times on first start-up in the morning, the exhaust may smell like “rotten eggs”. This is due to rich fuel condition with a cold engine. However, as the engine warms up, this smell should go away. If it does not, converter damage could possibly follow with extended driving.
